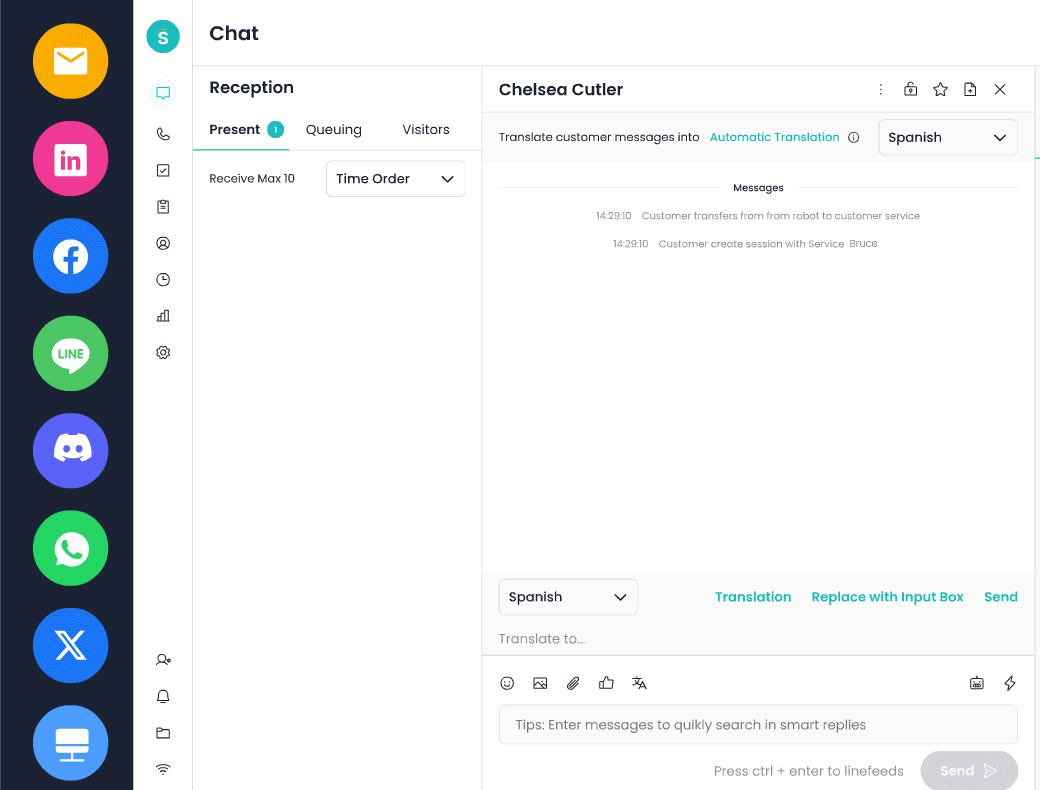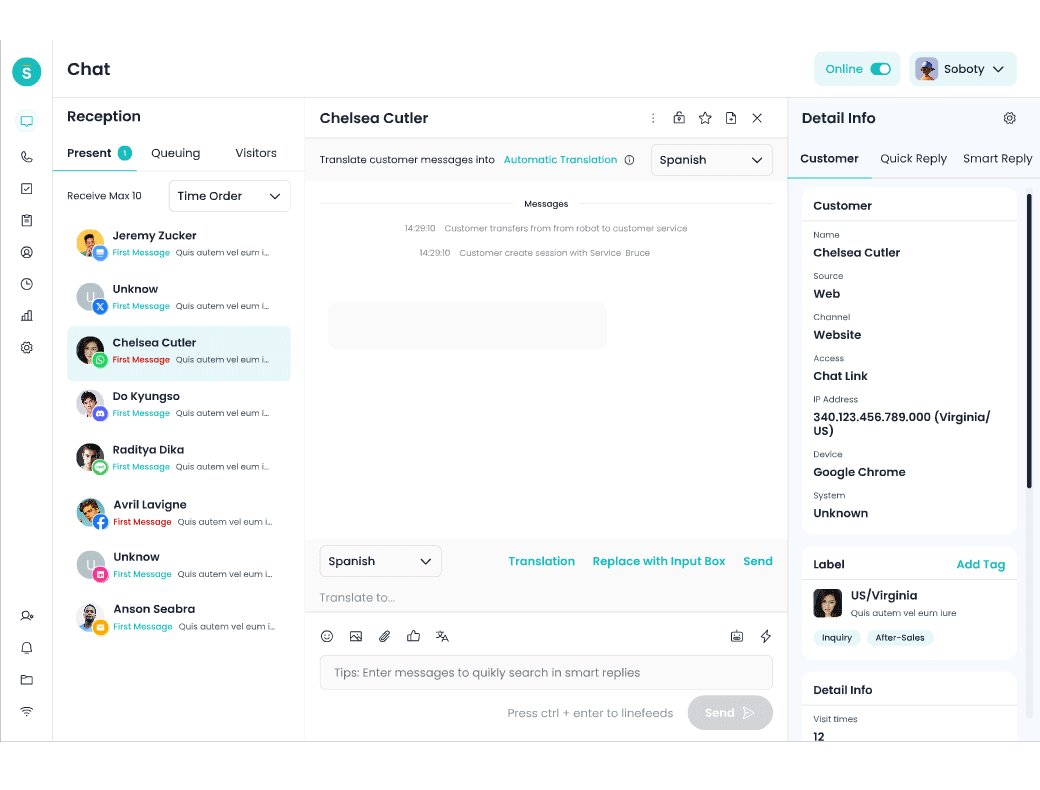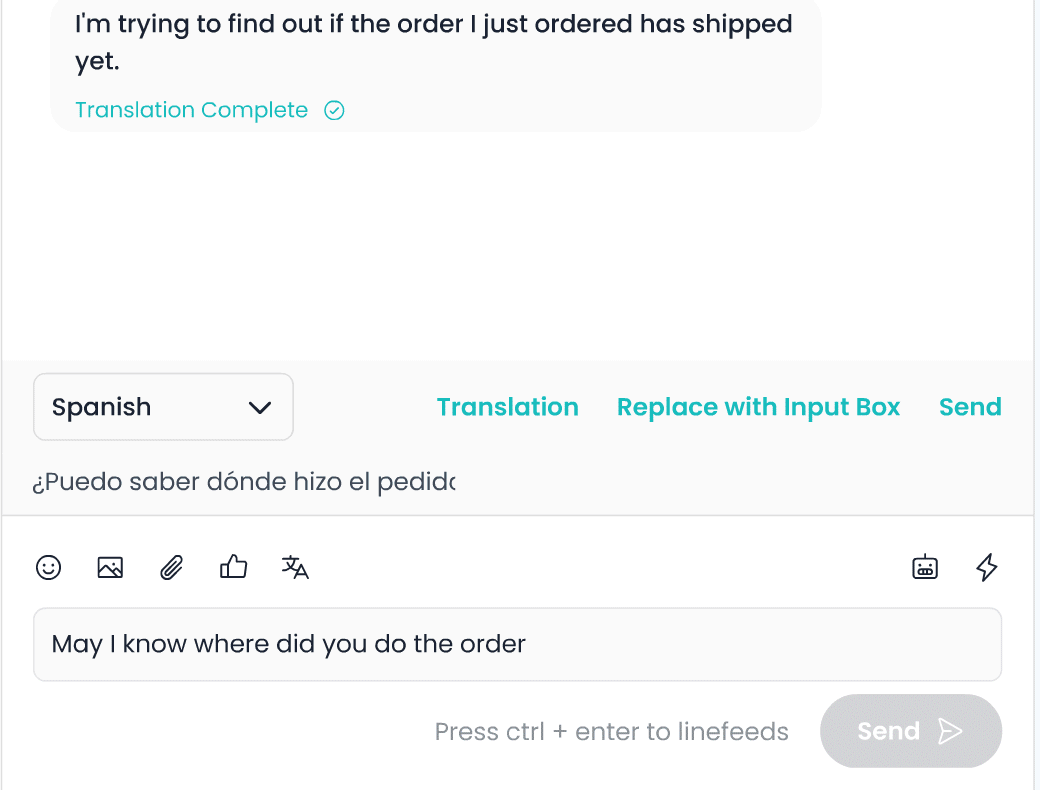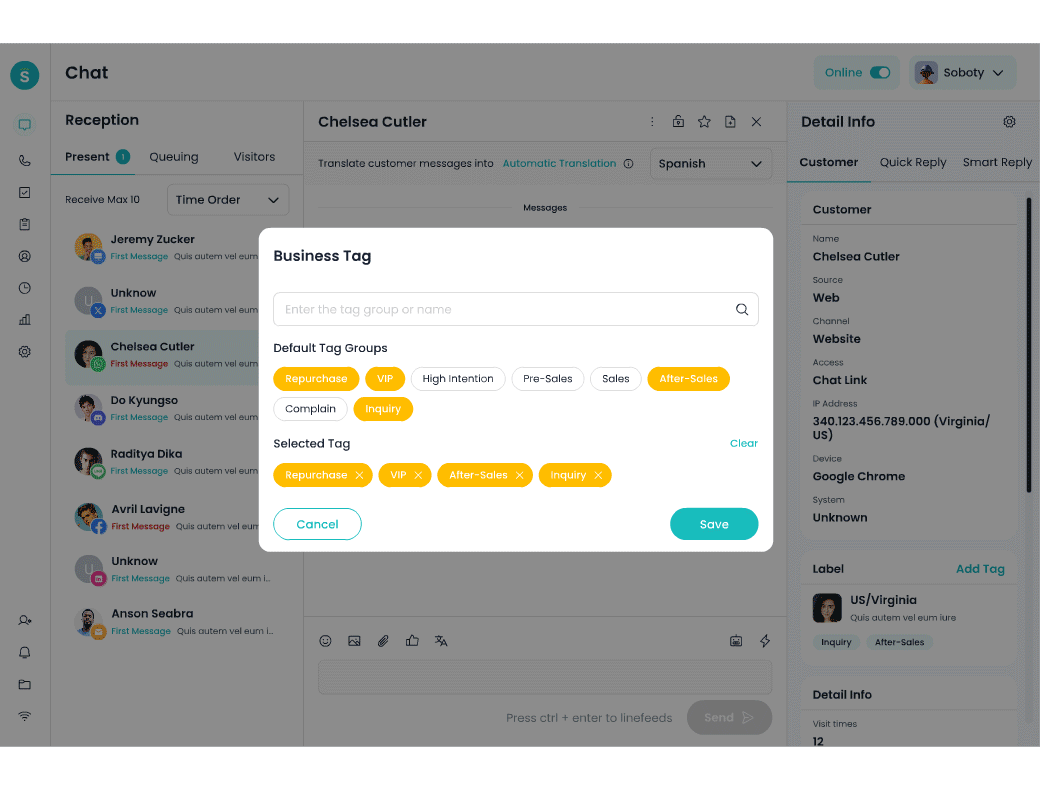
Imagine calling a company’s customer support line in the early 2000s. After navigating through a maze of menu options in an Interactive Voice Response (IVR) system, you finally reach a human agent—only to be placed on hold for several minutes. When your turn arrives, the agent asks for your details again, despite you entering them earlier.
Emails take days to receive a response, and live chat is almost nonexistent. Customer frustration is high, and businesses struggle to manage growing service demands.
Fast forward to today—AI-powered customer service has transformed this experience entirely. Intelligent chatbots provide instant responses, voice assistants handle queries with near-human accuracy, and AI-driven ticketing systems ensure seamless issue resolution. Companies now leverage machine learning (ML), natural language processing (NLP), and deep learning to deliver faster, more personalized, and efficient customer support.
Early Applications of AI in Customer Service
The history of AI in customer service is a story of innovation, with each technological milestone addressing key inefficiencies in customer support. The initial attempts at automation, though limited, paved the way for today’s advanced AI-driven systems.
Chatbots: From ELIZA to Q&A-Based Systems
The journey of AI in customer service 1960s with the creation of ELIZA, one of the first chatbots developed at MIT. ELIZA was a simple pattern-matching program that simulated human conversation by reformulating user inputs into pre-defined responses. While revolutionary at the time, it lacked real comprehension and was limited to scripted interactions.
Problems Solved:
- Basic query handling: Automated responses to frequently asked questions (FAQs), reducing the need for human agents.
- 24/7 availability: Provided constant customer interaction without requiring human presence.
Q&A-Based Chatbots and Their Limitations
Before the rise of modern Natural Language Processing (NLP), chatbots were primarily rule-based systems that relied on pre-programmed question-answer pairs. These bots worked well for structured queries but failed when faced with variations in phrasing or complex inquiries.
- Example: In early e-commerce, chatbots were used to retrieve order status based on predefined templates, but they struggled with context-aware queries (e.g., “Where is my package?” vs. “I didn’t receive my order yet”).
- Real-World Advancement: Comcast’s “Ask Me Anything” feature allowed customer service agents to query a large language model (LLM) in real-time, reducing conversation handling time by 10% (org).
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Systems: The First Phone Automation
In the 1980s, Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems emerged as a groundbreaking solution to reduce call center congestion by automating menu-based customer interactions over the phone. These systems allowed customers to navigate service options using either keypad inputs or voice commands.
Problems Solved:
- Call routing automation: Directed customers to the correct department, reducing wait times.
- Self-service transactions: Enabled users to perform simple tasks like checking account balances or making payments without human assistance.
Challenges and Limitations:
- Frustrating user experience: Early IVR systems had rigid menu structures, requiring customers to press numbers for specific options (e.g., “Press 1 for account information”). If their issue didn’t fit the available choices, they often got stuck in endless loops, unable to reach a real person.
- Limited voice recognition: Early voice command systems struggled to accurately understand different accents, speech variations, and background noise, leading to frequent errors and frustration.
🔹 Example: Many early banking hotlines used IVR systems to handle balance inquiries, but customers often got frustrated when misrouted or unable to connect with a live agent.
Email Automation: Scaling Customer Support in the Digital Age
By the late 1990s and early 2000s, businesses faced overwhelming volumes of customer emails. Handling inquiries manually became impractical, leading to the development of email automation systems that could sort, prioritize, and respond to messages without human intervention.
Problems Solved:
- Efficient sorting: Automatically categorized emails based on keywords (e.g., “refund” → billing team).
- Auto-replies: Sent instant responses for common inquiries, improving response time.
- Reduced agent workload: Allowed human agents to focus on complex issues rather than repetitive questions.
🔹 Example: Early customer service teams used rule-based email filters to automatically reply to refund requests, cutting down response times from days to minutes.
These early AI applications, despite their limitations, were pioneering steps in automating customer support. While chatbots, IVR, and email automation addressed fundamental challenges in scalability and efficiency, they also highlighted the need for more context-aware, flexible AI solutions—a gap that modern AI-driven platforms like Sobot have successfully bridged.
Evolution and Key Milestones of AI in Customer Service
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into customer service has transformed the way businesses interact with their customers. This evolution is marked by major technological advancements, shaping customer support from basic rule-based automation to highly sophisticated AI-driven solutions.
1960s–1970s: The Dawn of Automated Interactions
The journey began in the 1960s with the development of ELIZA, one of the first chatbots created by MIT’s Joseph Weizenbaum. ELIZA used simple pattern-matching techniques to simulate conversations, showcasing the early potential of AI in customer service. However, it lacked true understanding and adaptability.
During this era, early Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems were also introduced, allowing customers to interact with basic automated phone menus. These systems, though revolutionary, were rigid and frustrating due to their inability to process natural language.
1980s: The Rise of IVR Systems
The 1980s saw IVR technology become more widespread. Businesses implemented these systems to handle customer inquiries over the phone, reducing dependency on human agents. However, due to their limited flexibility, customers often found them frustrating, as they could only follow pre-programmed decision trees.
1990s: The Advent of Email and Early Automation
As businesses moved online in the 1990s, email became a critical communication channel. Early email automation tools emerged, allowing companies to sort messages and send predefined responses based on keyword detection. While this improved efficiency, the lack of contextual understanding often resulted in impersonal and irrelevant replies.
Late 1990s–Early 2000s: Emergence of Live Chat and Chatbots
The late 1990s and early 2000s brought a new wave of digital support: Live Chat. Websites began integrating real-time chat support, allowing businesses to assist customers instantly.
At the same time, early chatbots evolved, utilizing rule-based models and pre-set question-answer pairs to provide automated responses. While they improved response times, they struggled with complex, open-ended questions.
2010s: Integration of AI and Machine Learning
The 2010s marked a major leap in AI-powered customer service. With advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML), chatbots became more intelligent, capable of understanding customer queries in a more contextual manner. AI-driven automation allowed companies to provide 24/7 support, reduce response times, and offer personalized interactions.
During this period, Sobot started researching AI-driven customer service solutions in 2014, focusing on chatbot automation, ticketing systems, and omnichannel support. As AI technology evolved, businesses began leveraging machine learning models to analyze customer queries, predict user intent, and deliver more accurate, real-time responses.
2020s: The Era of Omnichannel AI Support
The 2020s have seen AI evolve into an integral part of customer service. Today’s AI-driven platforms use:
- Conversational AI & Generative AI to provide context-aware, human-like responses.
- Predictive Analytics to anticipate customer needs before they arise.
- Omnichannel AI for seamless support across chat, email, social media, and phone.
- Real-time Sentiment Analysis to gauge customer emotions and adapt responses accordingly.
Sobot remains at the forefront of these advancements, refining its AI models to enhance customer interactions and automate complex workflows.

Looking Ahead
The journey of AI in customer service continues, with emerging technologies pushing boundaries further. As AI-powered platforms like Sobot continue to innovate, businesses that embrace these advancements will gain a competitive edge in delivering efficient, intelligent, and personalized customer support experiences.

Recent Developments and Future Trends in AI Customer Service
The rapid advancement of AI technology continues to redefine customer service, introducing innovative solutions that improve efficiency, enhance personalization, and elevate the overall customer experience. From self-service AI tools to predictive analytics and generative AI, modern businesses are leveraging AI-driven solutions to optimize support operations.
AI-Driven Self-Service Solutions
AI-powered self-service platforms have become an essential component of modern customer support, allowing users to resolve issues without human intervention.
Intelligent Chatbots and Knowledge Bases: AI-driven chatbots and dynamic knowledge bases provide instant access to accurate information, reducing the burden on human agents.
Key Benefits:
- Immediate Resolution: Customers get answers without waiting.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for large customer support teams.
- Scalability: Handles thousands of queries simultaneously.
Predictive Analytics and Proactive Support
Predictive analytics is reshaping customer service by identifying potential issues before they arise.
- Data-Driven Insights: AI analyzes historical interactions and customer behavior to predict future inquiries and complaints.
- Proactive Engagement: Companies can resolve potential concerns before customers even reach out, improving satisfaction and loyalty.
- Technical Insights: Machine learning models detect patterns and anomalies, helping businesses optimize their support strategies.
Conversational AI and Generative AI
The rise of conversational AI and generative AI has transformed automated customer interactions, enabling machines to engage in more human-like conversations.
- Context-Aware Responses: Large language models (LLMs), like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, generate personalized and contextually relevant answers.
Key Advancements:
- Natural Interaction: AI mimics human conversation with remarkable accuracy.
- Scalability: Can handle millions of interactions simultaneously.
- Hyper-Personalization: AI tailors responses based on customer history, improving engagement.
Omnichannel AI Support
Customers now interact with brands across multiple channels—chat, email, phone, social media—requiring AI to provide a seamless experience.
- Unified AI Systems: AI integrates across platforms, ensuring consistent and personalized interactions.
Benefits of Omnichannel AI:
- Consistency: Ensures the same quality of support across different channels.
- Efficiency: AI can handle cross-channel interactions without losing context.
- Data-Driven: Aggregates customer interactions for better insights.
Emerging AI Trends Shaping the Future
While recent developments have revolutionized customer service, emerging AI trends promise even greater advancements in automation and personalization.
- Real-Time Sentiment Analysis: AI now detects customer emotions during interactions, allowing businesses to tailor responses for a more empathetic experience.
- AI-Powered Hyper-Personalization: Advanced AI models analyze user behavior, purchase history, and past interactions to deliver ultra-personalized support.
- Generative AI for Autonomous Support: With continued advancements in generative AI, customer service will shift toward fully AI-driven interactions with minimal human involvement.
- AI-First Support Platforms: Future customer service solutions will be entirely AI-powered, with virtual assistants handling most queries and humans only intervening in complex cases.
Sobot Use Case: AI-Driven Customer Support Innovation
As one of the early adopters of AI in customer service, Sobot has continuously innovated to enhance customer support efficiency.
- Comprehensive AI Support: Sobot integrates automated ticketing, live chat, and omnichannel support into a single AI-powered platform.
Real-World Impact:
- Automated Ticketing: AI categorizes and resolves tickets faster.
- Advanced Chat Automation: Provides intelligent, real-time responses to customer inquiries.
- Unified Dashboard: Offers a 360-degree view of customer interactions for better decision-making.
Sobot’s commitment to AI-driven customer service highlights the transformative power of automation. As AI continues to evolve, platforms like Sobot will play a crucial role in defining the future of intelligent customer support.

Conclusion
The evolution of AI in customer service highlights the power of technological innovation. From early rule-based chatbots like ELIZA to today’s sophisticated, context-aware systems, AI has redefined customer support. We explored its journey—from IVR and email automation to AI-powered live chat, voicebots, and automated ticketing systems.
Modern platforms now leverage ML, NLP, and LLMs for personalized, real-time, omnichannel support. Pioneers like Sobot, with research dating back to 2014, showcase how continuous innovation drives industry leadership.
As businesses increasingly focus on customer experience, AI’s role in support operations will only grow. Embracing AI-driven solutions is essential for companies aiming to boost efficiency, improve customer engagement, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving landscape.

FAQs
How is AI technology applied to Sobot contact center solution?
There are many AI applications in Sobot contact center solution.
1. For different roles: AI agents can receive customers, naturally communicate with them to solve common problems; AI Copilot assists agents in improving efficiency; AI Insight supports administrators to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the overall business, customer concerns, and team status.
2. For different contact ways: There are AI chatbot in online chat, and AI voicebot in calling.
For more specific functions, please feel free to contact us for a detailed understanding.
What are AI Agents?
AI agent is considered as a major breakthrough in AI, especially after it is combined with LLM.
To conclude, AI agent is a software program that can understand customer intentions, collect and process customer data, and ultimately provide feedback to customers or perform tasks. Human set goals and pose questions, and AI agent can independently choose the best way to achieve these goals.
What’s the core technology of Sobot’s Chatbot? Is it supported by the latest ChatGPT technology?
With NLP as its core technology, Sobot chatbot has become increasingly mature in underlying models and abundant in Q&A corpus after 10 year’s development.
Sobot chatbot also combines the emerging LLM technology of ChatGPT.
Currently, Sobot supports enterprises to upload knowledge documents and allows chatbot to learn independently to serve customers. Therefore, you can also call it “AI agent”.