LLMs (Large Language Models) represent a severe breakthrough in the area of NLP and AI. Models such as GPT-4 and BERT can already create human texts simply by using an immense amount of data and algorithms. Scale is the main characteristic of LLMs, and it allows them to capture elaborate patterns and fine subtleties of languages, which opens a wide range of applications.
Historical Background: Deeper Inside the Traditional Language Model
Traditional language models relied on more straightforward statistical methods and smaller data sets. These models used various methods, including n-grams and rudimentary rule-based text processing. With increased computational power and higher data availability, more complex models led to the creation of LLMs. Moving from these traditional models to LLMs required deep learning methodology to be baked into the complex algorithms that utilized large amounts of data for improved comprehension and language generation.
Definition and Structure
The definition of LLMs includes a large scale, which refers to the number of parameters and layers of the model. The “large” in their name lets them learn and represent some quite complex patterns in language. Typically, an LLM consists of a multi-layer neural network architecture, each responsible for different language processing aspects. Their architecture’s large number of parameters enables an LLM to process various language tasks with high accuracy.
Components
- Layers: These are the multiple neural network layers that make up an LLM. Each layer is related to various degrees of abstraction of text representation. These layers allow the model to process or generate text at different levels.
- Parameters: Parameters are internal variables learned by the model through training. LLMs have a billion parameters, which add to their ability to understand and generate realistic text.
- Training Data: The models are trained on massive datasets that include vast text sources. Such varied training data allows the model to learn the pattern of languages and contexts, improving performance across various tasks.
How Does an LLM Work?
LLMs process the input text by passing it through its layers and applying learned patterns and parameters. In this way, attention mechanisms within the model focus attention on different parts of the text to capture context or word-to-word relations. The output comes based on patterns learned from its training and, therefore, enables an LLM to generate, translate, or summarize text.
Overview of Architecture: Transformers
Many large language models are based on transformer architecture, which has brought new mechanisms to light, such as self-attention, to revolutionize NLP. Transformers enable the model to process text parallelly and capture long-range dependencies, further enhancing its performance in understanding and generating text. The transformer architecture is among the critical ingredients of recent LLMs, which have powered their efficiency for many complicated tasks involving languages.
Difference Between NLP and LLM
| Aspect | Natural Language Processing (NLP) | Large Language Models (LLMs) |
| Definition | A field of AI focused on enabling machines to understand and process human language. | A type of deep learning model designed to generate and understand text by processing large datasets. |
| Scope | Involves various tasks like text classification, sentiment analysis, translation, etc. | Primarily focused on language generation, comprehension, and prediction. |
| Model Complexity | May involve simpler models (like rule-based systems or traditional ML models) depending on the task. | Typically involves deep neural networks with billions of parameters, like GPT-3 or GPT-4. |
| Data Requirement | Can work with smaller, task-specific datasets. | Requires massive datasets (often terabytes of text) for training. |
| Application | Used for a wide range of language-related tasks across different industries. | Primarily used for tasks like text generation, chatbots, and large-scale language understanding. |
Applications and Use Cases of Large Language Models
LLMs can be applied to a wide array of fields, including:
- Content Creation: Writing articles, stories, and marketing materials. LLMs can produce coherent and contextually relevant content with input provided by prompts.
- Translation Summarization: accurate translation from one language to another. LLMs improve translation services by capturing nuances and context more accurately.Summarization involves providing concise summaries of longer texts. LLMs can summarize information without sacrificing important points and context.
- Conversational Agents: LLMs power chatbots and virtual assistants, allowing the conversational agent to understand and respond to user queries interactively and naturally.
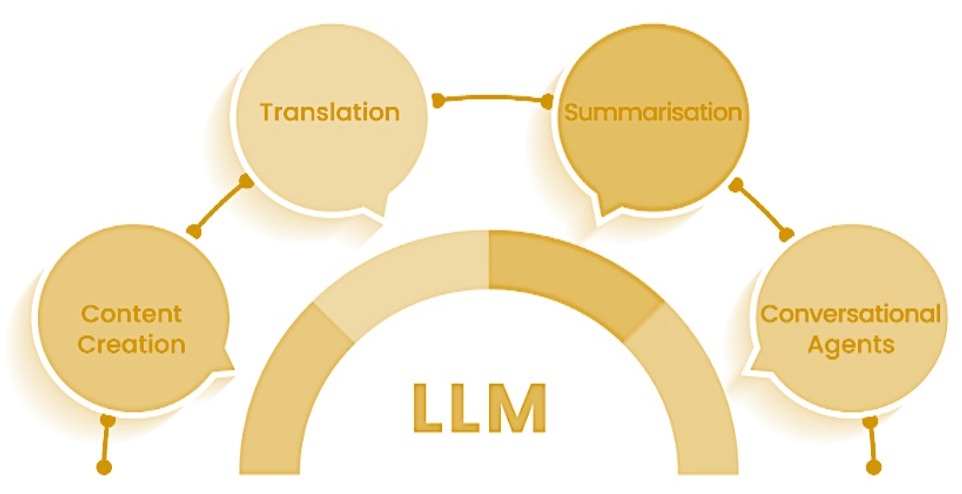
Overview of the Applications of LLM
The Role Applied Among Research and Development Activities Across Industries
LLMs are leading the latest research and development in healthcare, finance, and entertainment. They advance the field of language technology in contributions to innovations in AI applications and underpin new tools and service development. Researchers and developers look to LLMs to test new language processing and generation possibilities.
How LLMs are Changing Healthcare, Finance, and Entertainment
- Medical Care: LLMs contribute to medical record analysis, report generation, and patient support. They enhance the speed and precision of healthcare services.
- Finance: They support financial analysis, report generation, and customer service in this industry. They enhance decision-making and smoothen processes within the financial industry.
- Entertainment: LLMs help with content creation, scriptwriting, and interactive experiences within the industry. This knowledge can be used to make entertainment experiences more interactive and personalized.
Challenges
- Computational Costs: Training and deploying LLMs is so computationally expensive that it becomes very costly and resource-intensive.
- Environmental Impact: Energy consumption regarding LLMs has also raised environmental impact concerns. Efforts are underway to make these technologies greener.
- Bias and Fairness: An LLM could develop biases due to the nature of the training data used to create the model, which is a severe concern regarding its output’s fairness. This area is considered very important in addressing bias.
Data Protection and Privacy Discussion
LLMs should be sensitive to private information to ensure data protection and privacy. With their recent improvements, there is a threat that they can be used for malicious activities or unauthorized use. In this respect, robust data protection measures must be ensured for credibility and integrity.
New Trends Developed in LLMs
- GPT-4: This has been developed as an advanced version of the GPT series with enhanced language capability and superior performance.
- BERT: A model that focuses on understanding the text’s bidirectional context to improve the comprehension of natural language.
The Potential Impact Quantum Computing Has on LLMs
Quantum computing has much to do with LLMs and can turn everything upside down by being more computationally intensive, thus offering faster training times or better overall performances. Quantum algorithms could include the effective processing and management of large-scale data.
What LLMs Can Do to Shape the Future
The LLMs will continue to shape the future of AI; such applications secure further advances in language technology and widen the horizons for a new relationship between man and computer. They will be the core of the transformation in how we interact with and use language-based technologies.
The large language model stands out as one of the most significant miracles of AI and is influential in language understanding and generation. With the fast tempo of technological changes, it’s crystal clear that LLMs will change many other industries in the coming years, solve many challenges, and shape the future of AI.